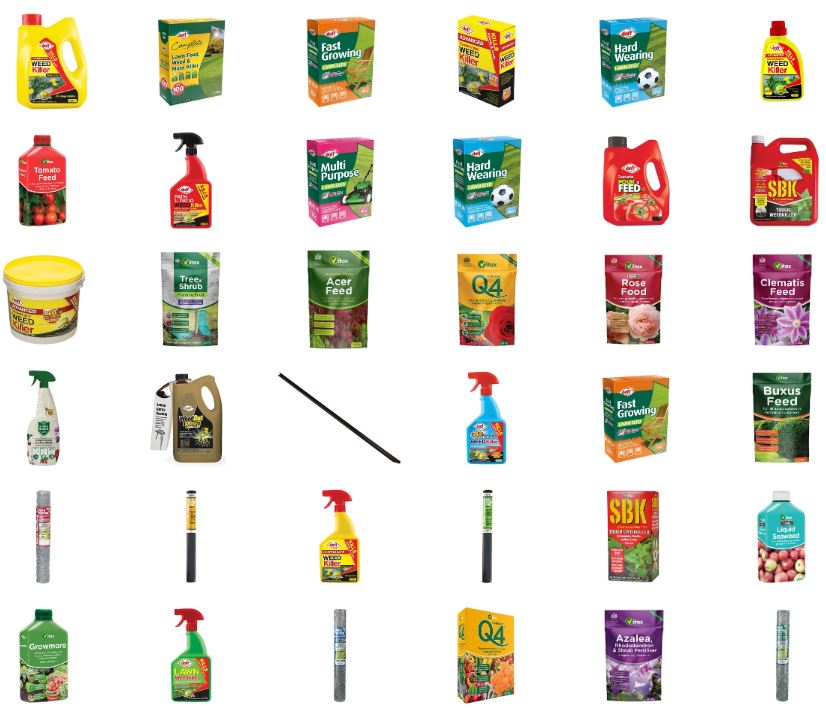
Gardening is more than a hobby—it’s an art and a science that brings beauty, health, and joy to our lives. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, using the right tools and techniques can make a world of difference. In this guide, we’ll explore four gardening essentials—weedkillers, feed, seed, and propagators—and offer practical tips for maximizing their effectiveness.
1. Tackling Weeds with the Right Weedkiller
Weeds are the nemesis of any gardener, stealing nutrients, sunlight, and water from your plants. The secret to managing them lies in choosing the right weedkiller and applying it effectively.
Types of Weedkillers:
- Selective Weedkillers: These target specific weeds without harming other plants, making them ideal for lawns.
- Non-Selective Weedkillers: Designed to eliminate all vegetation, they are best used for clearing areas entirely.
- Pre-Emergent Weedkillers: These prevent weed seeds from germinating and work well as a preventative measure.
- Post-Emergent Weedkillers: Effective for tackling mature weeds that are already growing.
Application Tips:
- Choose the Right Weather: Apply weedkiller on a dry, calm day to prevent it from washing away or drifting onto desirable plants.
- Follow the Instructions: Overusing weedkiller can harm the environment and neighboring plants.
- Spot Treat: For isolated weeds, use a targeted spray or applicator to minimize waste.
- Consider Natural Alternatives: Vinegar, boiling water, and mulching are eco-friendly solutions for smaller infestations.
2. Feeding Your Plants for Optimal Growth
Plants, like humans, thrive on a balanced diet. Garden feed delivers essential nutrients—nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)—to boost growth, health, and yield.
Types of Garden Feed:
- General-Purpose Fertilizers: Ideal for most plants, these provide a balanced mix of NPK.
- Specialist Fertilizers: Tailored for specific plants like roses, tomatoes, or lawns.
- Organic Fertilizers: Compost, manure, or bone meal that enrich the soil naturally.
- Liquid Fertilizers: Quick-acting and easy to apply through watering cans or hose attachments.
- Slow-Release Granules: Offer steady nourishment over weeks or months.
Feeding Tips:
- Test Your Soil: Use a soil testing kit to determine nutrient deficiencies and tailor your feed accordingly.
- Feed at the Right Time: Early morning or late afternoon feeding helps plants absorb nutrients without evaporation.
- Don’t Overfeed: Excess fertilizer can burn roots or lead to nutrient imbalances.
- Combine with Organic Mulch: Mulching retains moisture and provides additional nutrients as it decomposes.
3. Seeding for Success
Seeds are where it all begins—a tiny packet of potential waiting to flourish into flowers, fruits, or vegetables. Selecting the right seeds and planting them correctly can make or break your gardening journey.
Choosing Seeds:
- Certified Seeds: These are guaranteed to be disease-free and of high quality.
- Heirloom Seeds: Perfect for gardeners who value taste, tradition, and biodiversity.
- Hybrid Seeds: Bred for traits like disease resistance, uniformity, or improved yield.
- Wildflower Seeds: Great for creating a pollinator-friendly garden.
Seeding Tips:
- Read the Packet: Seed packets provide valuable information on sowing depth, spacing, and timing.
- Prepare the Soil: Remove debris, loosen the soil, and mix in compost for a fertile bed.
- Mark Your Rows: Use strings or stakes to keep rows straight and organized.
- Water Consistently: Maintain moisture during germination, but avoid overwatering, which can rot seeds.
- Thin Seedlings: Once they sprout, thin overcrowded seedlings to give each plant ample space.
4. Propagators: The Gardener’s Secret Weapon
Propagators are invaluable tools for starting seeds, rooting cuttings, and creating optimal conditions for young plants. Whether you’re propagating succulents, vegetables, or ornamentals, these devices give your green thumb a head start.
Types of Propagators:
- Unheated Propagators: Affordable and suitable for hardier plants.
- Heated Propagators: Provide consistent warmth for germination in cooler climates.
- Propagator Kits: Often include seed trays, pots, and lids for convenience.
- DIY Propagators: Reuse plastic containers, egg cartons, or glass jars for an eco-friendly option.
Propagation Tips:
- Choose the Right Medium: Use seed compost or a soilless mix for better drainage and aeration.
- Maintain Humidity: Keep the lid on to trap moisture, but ventilate occasionally to prevent mold.
- Monitor Temperature: Most seeds germinate between 65–75°F (18–24°C), so adjust accordingly.
- Label Everything: It’s easy to forget what you’ve planted, so label trays or pots clearly.
- Harden Off Young Plants: Gradually expose seedlings to outdoor conditions before transplanting.
Additional Gardening Tips for Success
- Rotate Crops: Avoid planting the same crop in the same spot to reduce pests and soil depletion.
- Encourage Pollinators: Plant flowers like lavender and marigolds to attract bees and butterflies.
- Mulch Wisely: Organic mulch like bark or straw helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil quality.
- Invest in Tools: Quality tools like trowels, pruners, and watering cans save time and effort.
- Stay Consistent: Regular weeding, watering, and feeding keep your garden in top shape.
Conclusion
Gardening is a journey of patience, learning, and growth—not just for your plants but for you as well. By mastering the use of essential products like weedkillers, feed, seed, and propagators, you’ll be well on your way to creating a vibrant and thriving garden. Happy gardening!
Read more about gardening products –